
- PROCESSING ARRAY VS ARRAYLIST HOW TO
- PROCESSING ARRAY VS ARRAYLIST UPDATE
- PROCESSING ARRAY VS ARRAYLIST ARCHIVE
It's also tested with php7.3 using bash5. I note this as contrasting with the fact that PHP triggers an E_NOTICE about "Undefined offset" "if there aren't enough array elements to fill the list()", as attow documented for and here only noted in by Mardaneus.įor completeness, a bash(1) (v5.0 or 4.3 on macos10.13) cli test producing the same result for all my PHP-versions (installed via ) follows.
Setting it like does _not_ raise an E_NOTICE (or other error) and afaics effectively equals an of $var1,$varN.
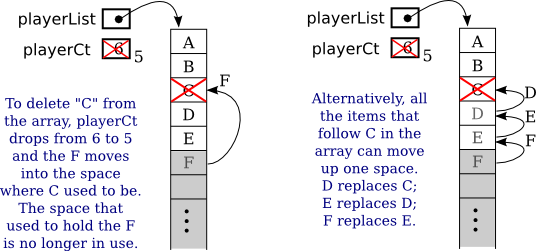
ArrayListPVector vectors new PVector 10 For a ArrayList you just declare the type it holds. When all space is consumed, and an additional element is to be added. Initialize with a string constant in quotation marks the compiler will size the array to fit the string constant and a string arraylist in androidassign values. Single/ Multi-Dimensional: Array can be multi-dimensional. Java provides the add() method to add elements in the ArrayList. You must be thinking how the Iterator checks for the modification, this is because the implementation of Iterator is present in AbstractList class where an int variable, modCount is present with the definition. Adding Elements: We can add elements in an array by using the assignment operator. From the output message, it is clear that the concurrent modification exception occurs when we try to call the iterator next() method.
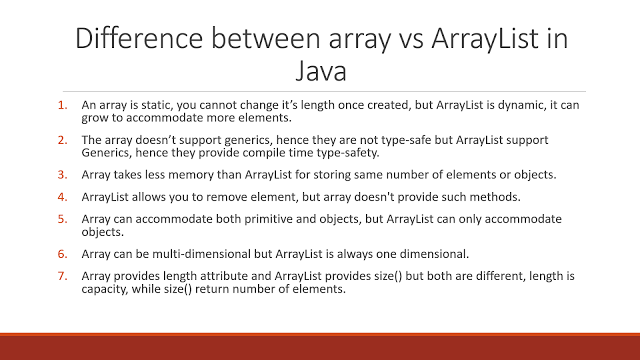
ArrayList provides the size() method to determine the size of ArrayList. If you use a normall array you must give it a size: Copy code. In computer science, a dynamic array, growable array, resizable array, dynamic table, mutable array, or array list is a random. Array provides a length variable which denotes the length of an array.
PROCESSING ARRAY VS ARRAYLIST ARCHIVE
The each method works in a similar fashion to for.Getting Started Introduction A simple tutorial Language Reference Basic syntax Types Variables Constants Expressions Operators Control Structures Functions Classes and Objects Namespaces Enumerations Errors Exceptions Generators Attributes References Explained Predefined Variables Predefined Exceptions Predefined Interfaces and Classes Context options and parameters Supported Protocols and Wrappers Security Introduction General considerations Installed as CGI binary Installed as an Apache module Session Security Filesystem Security Database Security Error Reporting User Submitted Data Hiding PHP Keeping Current Features HTTP authentication with PHP Cookies Sessions Dealing with XForms Handling file uploads Using remote files Connection handling Persistent Database Connections Command line usage Garbage Collection DTrace Dynamic Tracing Function Reference Affecting PHP's Behaviour Audio Formats Manipulation Authentication Services Command Line Specific Extensions Compression and Archive Extensions Cryptography Extensions Database Extensions Date and Time Related Extensions File System Related Extensions Human Language and Character Encoding Support Image Processing and Generation Mail Related Extensions Mathematical Extensions Non-Text MIME Output Process Control Extensions Other Basic Extensions Other Services Search Engine Extensions Server Specific Extensions Session Extensions Text Processing Variable and Type Related Extensions Web Services Windows Only Extensions XML Manipulation GUI Extensions Keyboard Shortcuts ? This help j Next menu item k Previous menu item g p Previous man page g n Next man page G Scroll to bottom g g Scroll to top g h Goto homepage g s Goto search I think that explenation is quite clear but ok, i will do a attempt. Ruby arrays are objects, and they provide the each method for working with elements.
We can then print the element’s value using puts. For each element in the sharks array, Ruby assigns that element to the local variable shark.

Notice that in this case the BaseType is an object whereas the above examples have BaseTypes of Arrays which exhibit inheritance from the Object class. Ruby provides the for.in syntax, which looks like this: sharks = Below you can see that you need to explicitly create an ArrayList object using the New-Object cmdlet or by casting a standard array to an ArrayList object. Not that it does anything different than youd do on your own (it just loops through every element and sets it to null).
PROCESSING ARRAY VS ARRAYLIST HOW TO
In this article, we’ll explore how to iterate over an array and display each of its elements. Ruby provides many ways to iterate over an array, and each method you use depends on the kind of work you want to perform. Now let’s look at how to work with all of the elements in the array.
PROCESSING ARRAY VS ARRAYLIST UPDATE
To make sure you update the right element, you could use the index method to locate the element first, just like you did to find the element you wanted to delete.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
